- Home
- Collections
- Atlas Resources for Schools
- Cork Fatality Register
- Mapping the Irish Revolution
- Mapping IRA Companies, July 1921-July 1922
- Mapping the Burning of Cork, 11-12 December 1920
- Martial Law, December 1920
- The IRA at War
- The Railway Workers’ Munitions Strike of 1920
- The Victory of Sinn Féin: The 1920 Local Elections
- The War of Words: Propaganda and Moral Force
- The IRA Offensive against the RIC, 1920
- De Valera’s American Tour, 1919-1920
- The British Reprisal Strategy and its Impact
- Cumann na mBan and the War of Independence
- The War Escalates, November 1920
- The War of Independence in Cork and Kerry
- The Story of 1916
- A 1916 Diary
- January 9-15 1916
- January 10-16, 1916
- January 17-23, 1916
- January 24-30, 1916
- February 1-6 1916
- February 7-14, 1916
- February 15-21, 1916
- February 22-27, 1916
- February 28-March 3, 1916
- March 6-13,1916
- March 14-20, 1916
- March 21-27 1916
- April 3-9, 1916
- April 10-16, 1916
- April 17-21,1916
- May 22-28 1916
- May 29-June 4 1916
- June 12-18 1916
- June 19-25 1916
- June 26-July 2 1916
- July 3-9 1916
- July 11-16 1916
- July 17-22 1916
- July 24-30 1916
- July 31- August 7,1916
- August 7-13 1916
- August 15-21 1916
- August 22-29 1916
- August 29-September 5 1916
- September 5-11, 1916
- September 12-18, 1916
- September 19-25, 1916
- September 26-October 2, 1916
- October 3-9, 1916
- October 10-16, 1916
- October 17-23, 1916
- October 24-31, 1916
- November 1-16, 1916
- November 7-13, 1916
- November 14-20, 1916
- November 21-27-1916
- November 28-December 4, 1916
- December 5-11, 1916
- December 12-19, 1916
- December 19-25, 1916
- December 26-January 3, 1916
- Cork's Historic Newspapers
- Feature Articles
- News and Events
- UCC's Civil War Centenary Programme
- Irish Civil War National Conference 15-18 June 2022
- Irish Civil War Fatalities Project
- Research Findings
- Explore the Fatalities Map
- Civil War Fatalities in Dublin
- Civil War Fatalities in Limerick
- Civil War Fatalities in Kerry
- Civil War Fatalities in Clare
- Civil War Fatalities in Cork
- Civil War Fatalities in the Northern Ireland
- Civil War Fatalities in Sligo
- Civil War Fatalities in Donegal
- Civil War Fatalities in Wexford
- Civil War Fatalities in Mayo
- Civil War Fatalities in Tipperary
- Military Archives National Army Fatalities Roll, 1922 – 1923
- Fatalities Index
- About the Project (home)
- The Irish Revolution (Main site)
The Rebel Garrisons in 1916
Map and Caption from the Atlas of the Irish Revolution (CUP 2017)
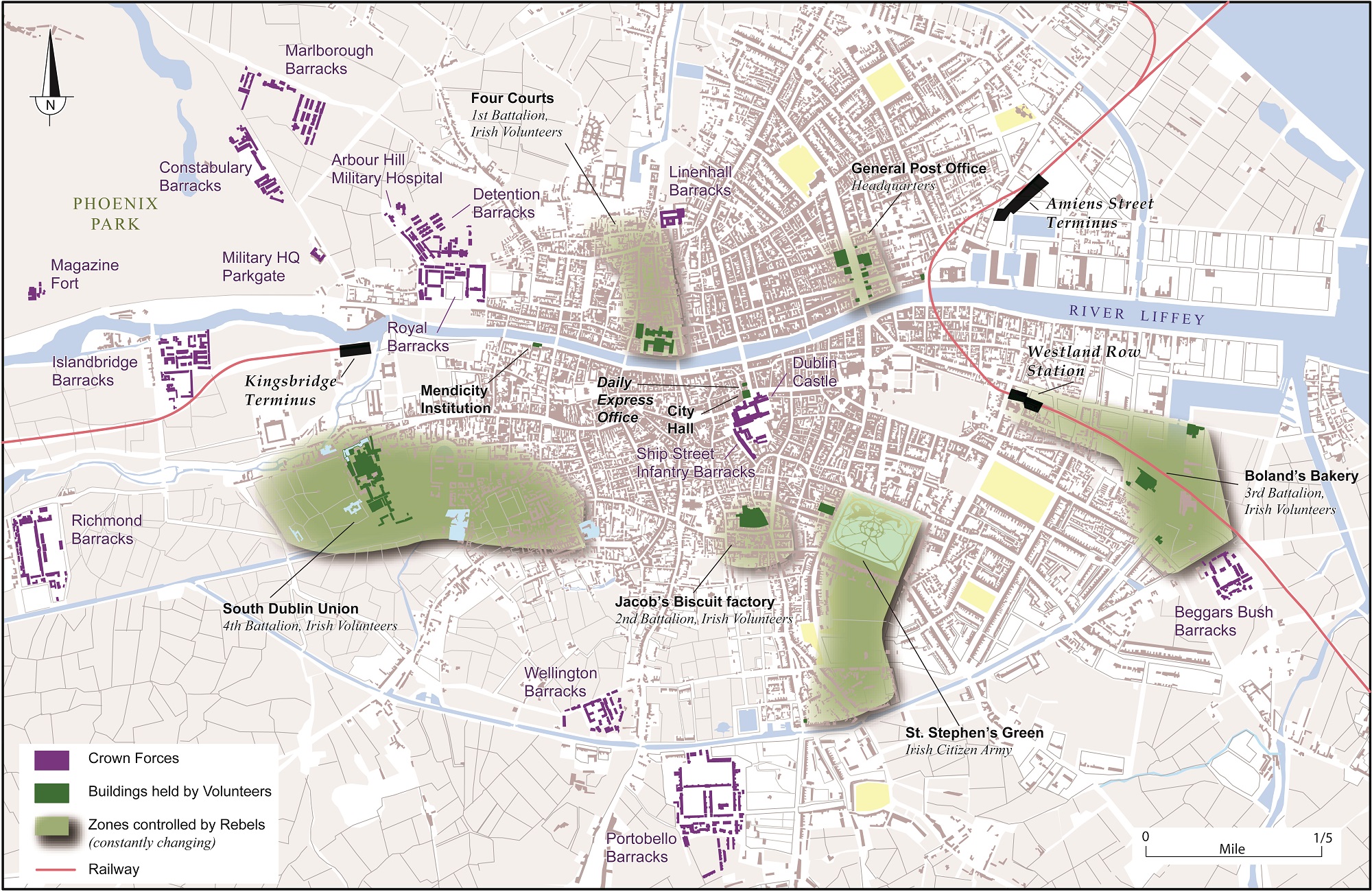
Though the Easter Rising was planned to be a national affair, IRB strategists primarily concentrated on seizing Dublin. They intended to hold the Irish capital as long as possible, in order to grab international attention and inspire future generations of Irish nationalists. The republican military plan ringed the city centre with interconnected strongholds, which could reinforce each other. Positions were selected to contain the numerous British Army barracks in the Dublin suburbs, and control major road and rail approaches into the city centre to be used by military reinforcements.
Irish Volunteers and members of the Irish Citizen Army (ICA) carried food, water, and picks to burrow between buildings. Street barricades would slow advancing troops, and subject them to republican fire from hidden positions in nearby buildings. Though heavily outnumbered and outgunned, the rebels knew the urban terrain, while their officers had months to select strategic firing points and defensive posts.
In terms of dispositions, the Irish Volunteer 3rd Battalion held the area around Boland’s Bakery, threatening Beggar’s Bush Barracks and an advance from Kingstown (Dún Laoghaire), the probable source of troop reinforcements arriving by ship from Britain. The ICA at Stephen’s Green stood astride a major crossroads into the heart of the city, which included a likely approach from Portobello Barracks. Another ICA unit would attack Dublin Castle and divert British troops to that locale, rather than allowing them to concentrate against rebel positions still being fortified. The 2nd Battalion headquartered in Jacob’s Factory could repel British advances from Wellington and Portabello Barracks, and target other reinforcements dispatched to Dublin Castle. The 4th Battalion in the South Dublin Union and surrounding areas covered Richmond and Islandbridge Barracks, as well as Kingsbridge Railway Station, a likely arrival point for military reinforcements. Across the river, 1st Battalion units in the Four Courts and King Street could frustrate approaches from the Royal and Marlborough Barracks; they could also provide the rebels with a possible line of retreat from the city, should the countryside rise up. A garrison with the Provisional Government group occupied the GPO and other strong buildings along Sackville Street. During the fighting, this basic plan allowed the rebels to seize Dublin, despite a low turnout of Volunteers and the presence of thousands of British troops within the wider area.
Significant success was achieved in places like North King Street, South Dublin Union and Mount Street Bridge, where the rebels conducted hit-and-run attacks on advancing British troops, or lured them into hidden pre-planned fields of fire. However, after a few days of fighting the weight of the British forces ultimately constricted the rebels, and pinned them into isolated positions that were then blasted by vastly superior British firepower. Considering the odds that were stacked against them, their five-day stand was about as much success as the rebel planners could have reasonably hoped for. [Source: Atlas of the Irish Revolution, (CUP, 2017]
