Surface wind speeds and directions from MERA
Previous posts have discussed software tools for extracting and visualising data from GRIB archives. With some help, I've used Panoply to read and visualise surface wind speeds from the sample Met Eireann Reanalysis (MERA) data files.
Separate GRIB archives of the u- and v- components of the horizontal surface (10 m) wind velocity are provided. Panoply can import multiple datasets and it can also be used to combine the u- and v- components in order to visualise surface wind speeds and directions. This page from NASA's Goddard's Earth Science Data and Information Services Center describes how to do this.
Here's an example of the output from 03:00, 1st June 2015, with prediction intervals of 1, 2 and 3 hours respectively:
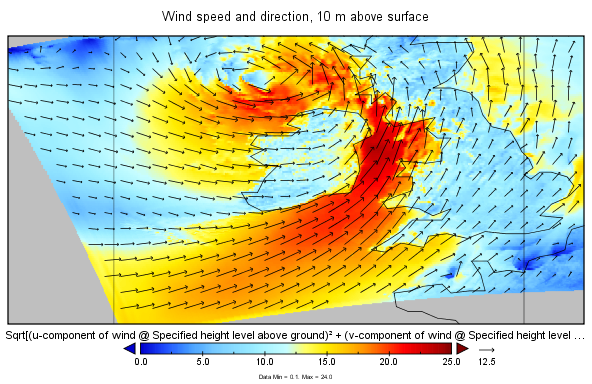
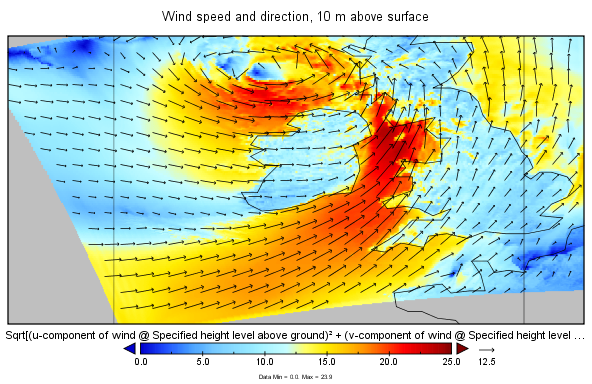
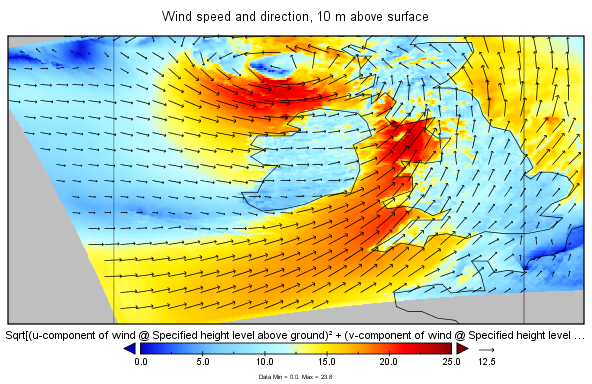
10 m surface wind speeds (m/s) and vectors from MERA from 03:00 the 1st June 2015, with prediction intervals of 1, 2 and 3 hours.
I'm still unsure of the timestamp convention. For each of these images, Panoply reported the "GRIB reference time" as 2015-06-01 15:00+0000. The corresponding "GRIB Forecast or Observation Time" entries are 2015-06-01 01:00+0000, 2015-06-01 02:00+0000 and 2015-06-01 03:00+0000. This is a bit confusing because the Forecast times appear to be before the reference time but I think it may just be a glitch in either the GRIB file or in how it is handled by Panoply. My interpretation is that these charts correspond to the model run for 2015-06-01 15:00 for prediction intervals of 1h, 2h and 3h, i.e. for 16:00, 17:00 and 18:00 on the same day as the model run. Met Eireann's paper from the European Meteorological Society Conference states that 3 hours of predictions are supplied for each model run, apart from the 00:00Z run.
Next step: to 'slice and dice' these data in order to get time series of wind speeds for a particular location. Panoply seems to be able to do this, but wgrib might be a bit more practical when it comes to larger datasets.
Electricity and Environment Laboratory
Renewable energy and land-atmosphere interactions research
Contact us
