DENiM H2020 EU Project
DENiM will develop an interoperable digital intelligence platform to enable a collaborative approach to industrial energy management. DENiM provides an integrated toolchain to provision advanced digital services including secure edge connectivity leveraging IoT, data analytics, digital twin, energy modelling and automation culminating in the delivery of continuous energy impact assessment, together with energy control and optimisation across existing production facilities, processes and machines. DENiM is based on three fundamental strategies to enable energy efficient management of manufacturing systems
Project website - https://denim-fof.eu/consortium/
BIM4EEB H2020 Project
BIM4EEB aims to foster the renovation industry by developing an attractive and powerful BIM management system with BIM-based toolset able to support designers in the design and planning phase, construction companies to efficiently carry out the work and service companies to provide attractive solutions for building retrofitting.
The BIM management system combined with the tools will also facilitate the decision making and the asset management for public and private owners due to the exploitation of augmented reality and the use of updated digital logbooks.
Project Webstie - https://www.bim4eeb-project.eu/the-project.html
ERBE CDT
The ERBE CDT brings together world-leading academics from established energy research centres at MaREI, Loughborough University (LU) and University College London (UCL).
The CDT will train the future innovators and leaders capable of driving the future energy transformation. Students are trained through a programme of taught courses and PhD research hosted by the leading energy research groups in the UK and Ireland.
The training is led by world-leaders in their field and spans the technical, social and economic aspects of energy in the built environment, including: new and renewable energy systems; energy storage; smart controls; data analytics; socio-technical systems; people-centred design; human behaviour and energy economics.
It aims to promote excellence in research through the training of cohorts of doctoral students and the fostering of collaboration between UK and Ireland based researchers.
Project Website - https://www.marei.ie/research/
M&V 2.0 for Industrial Facilities
This project focuses on research into the application of machine learning techniques to improve the accuracy of the measurement and verification (M&V) of energy savings in industrial facilities. The increased effectiveness of energy management has led to a vast quantity of energy data becoming available. However, the value of this data is rarely maximised when carrying out M&V. The objective of the research is to define a clear and methodical process for utilising data science tools in M&V while also streamlining the entire process. This project is headed by Colm Gallagher.
.png)
Data Analytics for Optimising Wind Turbine Performance
Wind turbine maintenance costs can reach 20 to 25 % of the total cost of energy generation over the lifetime of a turbine, so minimising these costs is essential. Usually, maintenance is carried out on a scheduled periodic basis (preventative maintenance), or following component failure (reactive maintenance). However, by using condition monitoring techniques to monitor the health of components, maintenance need only be performed when a component shows signs of deterioration. This means the turbine does not need to be taken offline for periodic inspections, saving valuable revenue.
In the wind industry, condition monitoring has usually peformed been by retrofitting expensive sensors to the turbine, but the results of this have been mixed. This project aims to instead leverage existing sources of data on the wind turbine, such as from the turbine's supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) system. Machine learning techniques are applied to historical failure identify trends and unique "fingerprints" in the data of what an impending fault looks like. Using existing data means that no expensive equipment needs to be retrofitted to the turbine, and the results are intended to be interpretable, foregoing the need for extensive signal analysis. This project is currently headed by Kevin Leahy.
Industrial Analytics Framework
This research focuses on the development of an industrial analytics framework to support the development of data-driven engineering informatics applications. Industrial analytics is an important aspect of smart manufacturing that employs data-driven methods, tools and technologies to inform decision-making. Many technologies that exist in the industrial analytics ecosystem originate from mainstream information technology, before adaptions are applied to facilitate their use in industrial environments. Such mainstream technologies include Big Data, Machine Learning and Internet of Things (IoT), to name a few. Developing industrial analytics capabilities centres on the application of these technologies, coupled with systematic cross-factory convergences governing Operation Technology, Information Technology, Data Analytics and Embedded Analytics. Given the lack of formal theoretical frameworks to guide these transformations, this research provides a systematic and formal methodology for designing, developing and improving industrial analytics capabilities. This project is currently headed by Peter O’Donovan.
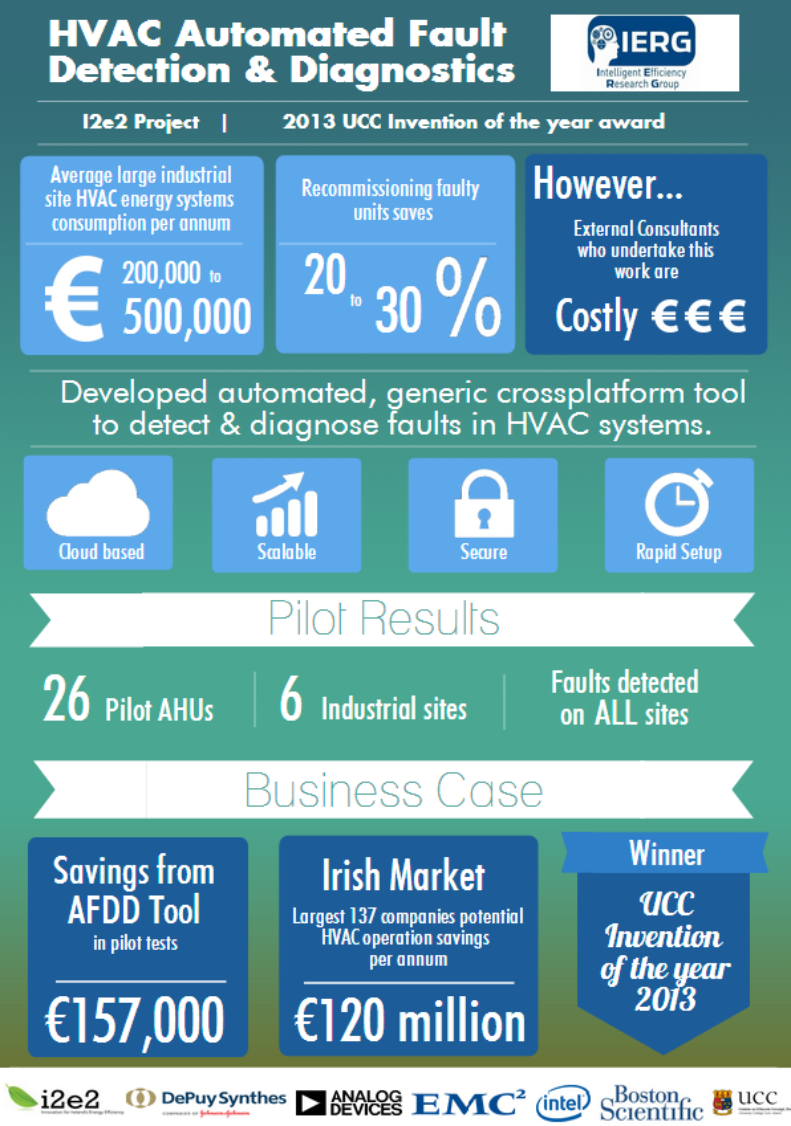
Automated Fault Detection for AHUs
View more detail on HVAC Automated Fault Detection & Diagnostics project
Carbon Neutral Buildings Project
View more detail on Carbon Neutral Buildings Project
Drive for Zero
The Drive4Zero is a unique and exciting initiative that aims to promote the use of electric vehicles in Ireland using Cork as a pilot area. This Drive4Zero initiative provides a real opportunity to leverage special savings, unique product offerings and a variety of advantages to convince more people that driving an electric car is the right choice for many reasons.
Several people, organisations, companies and groups have come together to make Drive4Zero a reality. The initiative has been spearheaded by Minister for Agriculture, Food & Marine with responsibility for Defence, Simon Coveney T.D., who is an electric car driver, electric vehicle (EV) ambassador and a passionate advocate of EVs.
For more information please click here
EMWiNS - Energy Monitoring Wireless Networked Systems
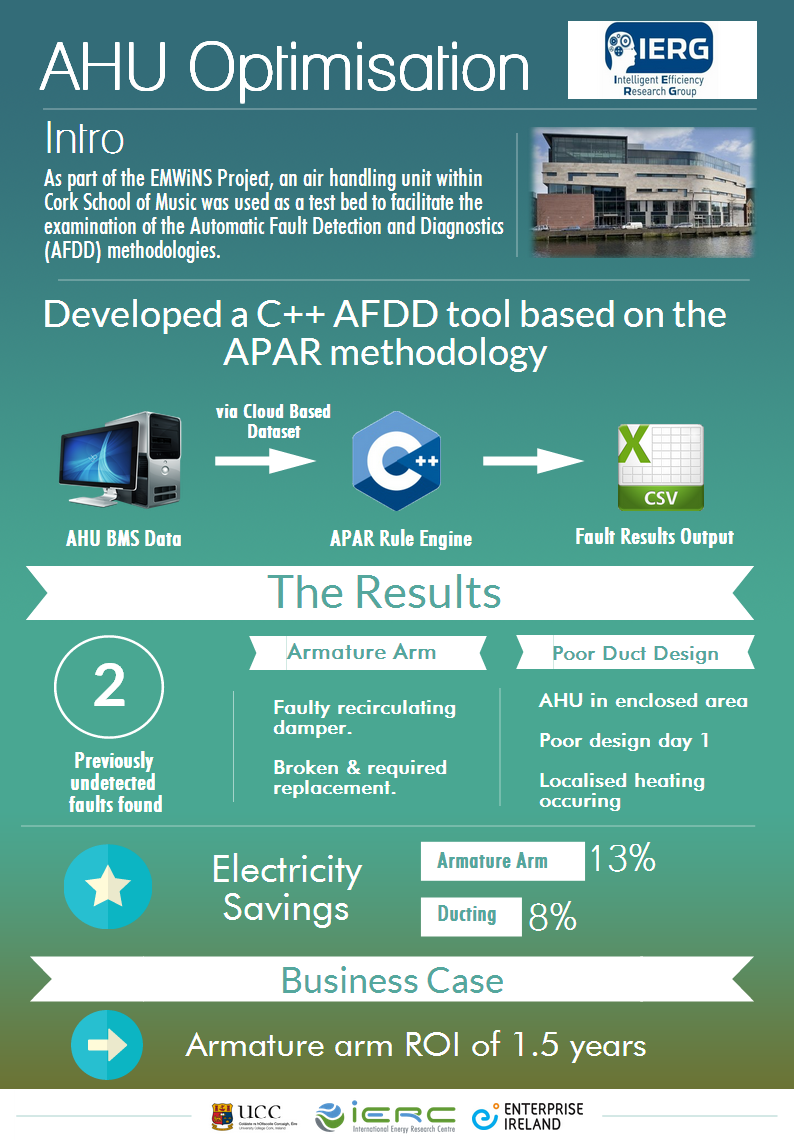
View more detail on EMWiNS - Energy Monitoring Wireless Networked Systems
Integrated Intelligent Energy/Water Management Systems
The management of Energy is one of the most important challenges facing the international community. As targets are set for reductions in greenhouse gas emissions and improvements in efficiency, cost reduction goals are also being imposed. The criticality of demand side management is now emerging, with energy efficiency widely accepted as being the first objective. It is argued that over half of the greenhouse gas reductions needed, should come from efficiency measures.
In parallel with Energy, Worldwide shortages in the availability of water of a suitable quality have now created a shift in focus towards its utilisation. Water is being proclaimed as "the new oil" with individuals and industries alike projecting ahead to the criticality and cost impact of this valuable resource. Whilst many countries have plans for a clean energy future, they must also plan for water scarcity and therefore the two efforts must be seen as one. Water and energy consumption are not always fully considered as two parts of the same issue, however it takes a considerable amount of water to produce electricity from most of the generation sources used today and it also takes a substantial quantity of energy to pump, deliver and clean water. Increasingly, the energy-water nexus cannot be ignored and indeed many water efficiency improvements save as much energy as some energy efficiency measures but at approximately half the cost. Within this overall research scheme, it is proposed to consider Water as a utility resource in a similar manner to other environmental energy streams.
Whilst it is generally accepted that improvements in water management are required worldwide, the relatively low apparent financial cost of water is inhibiting the essential changes. Motivating factors are necessary to enable the transformation and whilst standards such as ISO14046 Water Footprint and even ISO50001 Energy Management provide a framework to allow companies fulfil their corporate and social responsibilities, the cost savings associated with the necessary modifications do not alone provide adequate justification. The reason for this is that the true cost or true value of the water being used is not known and hence unappreciated.
In order to remedy this situation within industry, a novel framework for establishing the true cost of water by analysing the value added has been developed and its application to a typical manufacturing factory is being researched. The framework may also be similarly applied to other water life-cycle stages.
The true cost provides a valuable insight into the operation of the facility, a means for internal and external benchmarking and internal cost control, and also the data necessary to financially justify any modifications required. The data may also be used to assist with the calculation of a water footprint or a life-cycle cost.
Once the proposed methodology is implemented, changes will be possible which will result in water, energy and cost savings along with environmental benefits. Employment of this methodology, involving a Value System (VS) and a simulation model, would facilitate the application of Information and communications technology (ICT) to resource efficiency and thus may be used to assist in confronting necessary sustainability challenges.
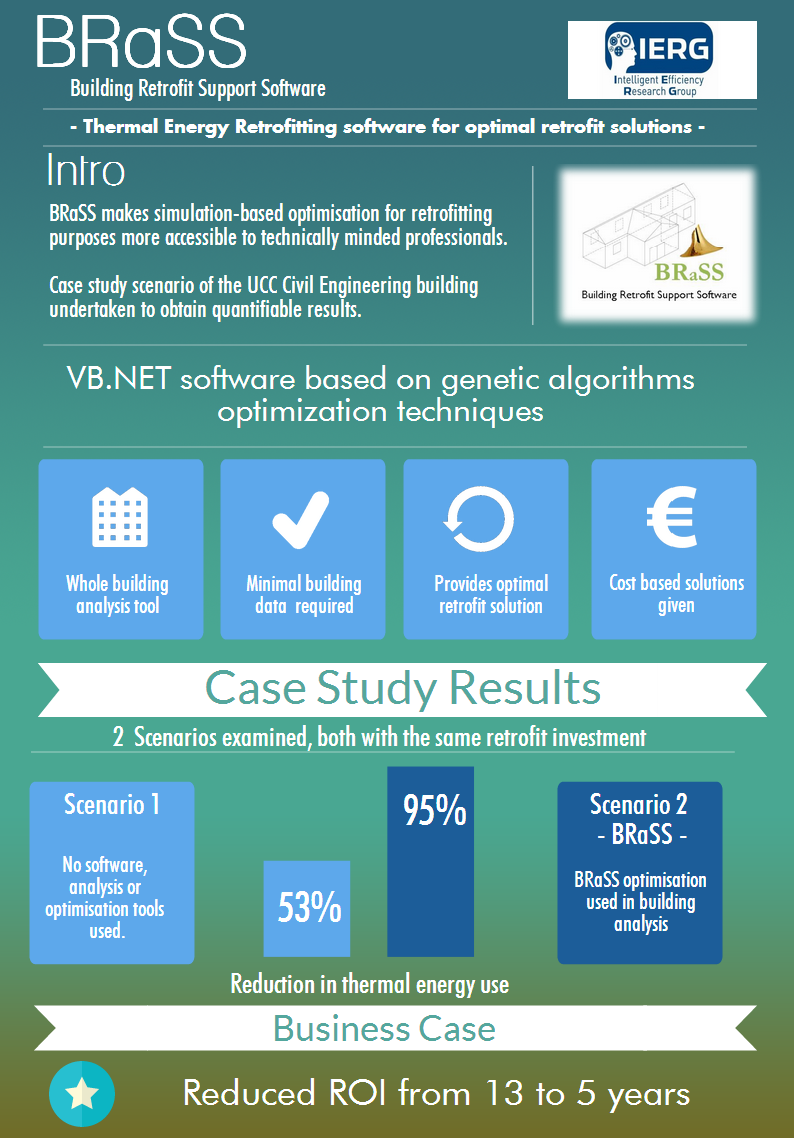
Appropriate Working Environments
The I2E2 Energy Research Centre is a government sponsored Technology Centre, established to facilitate research which will have a direct impact on industry. The I2E2 research focus is on energy efficiency improvements in factories, plant, equipment and buildings. The current research agenda focuses on compressed air systems characterisation, use and solution integration; appropriate work environments and HVAC systems. The innovations will enable the Irish manufacturing industry to improve competitiveness via breakthroughs in energy efficiency and cost reduction.
The aim of the IERG/i2e2 project is to investigate ways of reducing the cost of providing appropriate working environments for product, people and machines in Irish manufacturing plants (HVAC systems and clean rooms). Maintaining appropriate working conditions is costly. According to the SEAI Energy Agreements HVAS Special Working Group Report 2007, HVAC energy costs can be as high as 80% of a site’s total energy budget and, among the 14 companies which participated in the SEAI study, €15 million a year of savings were identified. Further dependency on cleanroom is increasing and the Carbon Trust has estimated that around 40% of commercial floor space could be air conditioned by 2020, compared to only 10% at the end of 1994.
As part of this three year project from 2011 to 2014, the IERG team have developed a software tool encompassing an expert analytics system which detects and diagnoses faults in HVAC system. To date, over €150,000 of energy savings have been identified on 7 pilot sites across 26 AHU's by the beta stage AFDD tool.
Thermal Energy Storage using PCMs in a Cooling System
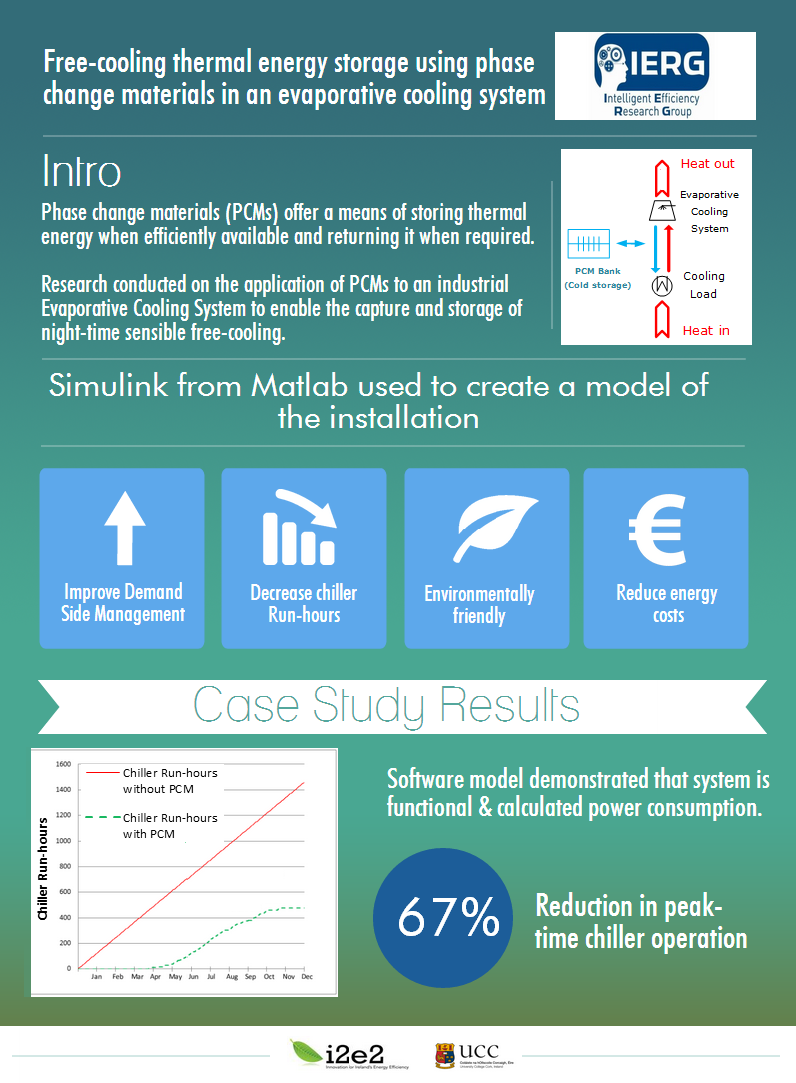
View more detail on Thermal Energy Storage using PCMs in a Cooling System Project
Decision Support Systems (DSS)
The development of Decision Support Systems (DSS) to facilitate energy performance improvement in large industry
The transition by industry to cleaner and smarter production is a crucial step in addressing the global challenge posed by climate change; the uptake of renewable sources of energy is key to this transition. In responding to this imperative, different industrial sectors has been implementing renewable energy projects for the last number of years. With more disparate generation, comes a need to effectively manage the integration of these systems. This has not always happened effectively when multiple systems are utilised on the same site, resulting in some renewable energy systems being sub optimally utilised due to a perception that they are not efficient when in fact it is their operation which has not been implemented efficiently to maximise their performance. This project, led by Dr Ken Bruton in partnership with DePuy Synthes, aims to integrate hybrid renewable energy supply (wind, chp, biomass etc) storage and efficiency with advanced and modular manufacturing. It will also deliver near real time analysis of linkages between process output and multi-source energy input enabling more effective decision making surrounding (global) asset operations.
The FLEX4FACT Project
The FLEX4FACT project aims to develop an end-to-end ecosystem based on a modular and multi-level architecture to enable flexible manufacturing in industries and create the conditions for the necessary energy transition in energy intensive industrial sectors.
In order to achieve the goals of the EU Green Deal and national energy agendas, there is an increasing need for flexibility to compensate for the fluctuating generation from renewable energy sources. The industrial sector is one of the largest consumers of energy, and increasing the flexibility of industrial processes, combined with on-site energy supply and storage technologies, can offer new opportunities to improve the sustainability of industrial sites and help integrate more renewable sources in the power grid.
FLEX4FACT aims to assist its industrial partners in achieving their energy transition by developing digital tools, integrated in a holistic platform, thus paving the way for industrial flexibility provision benefiting various stakeholders along the value chain. This will, in turn, increase the penetration of renewable sources, decreasing the dependency on energy fuels and helping to reduce the energy bills of EU enterprises.