Publications
Microplastics and cellulosic microparticles in North Atlantic deep waters and in the cold-water coral Lophelia pertusa
- Authors
Alicia Mateos-Cárdenas, Andrew J. Wheeler, Aaron Lim
- Year
- 2024
- Journal Name
- Marine Pollution Bulletin
- Category
- Journal Article
- Keywords
- MicroplasticsDeep-sea ecosystemsAnthropogenic pollutantsCold-water coralsNE Atlantic
- Link to Publication
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0025326X24007185
Abstract
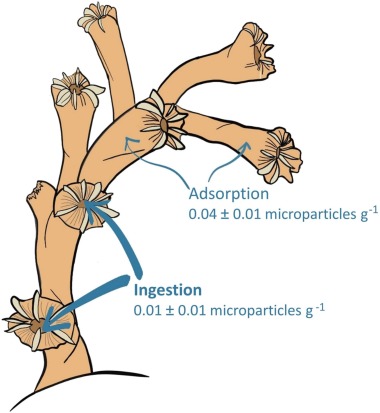
This study explores microplastic and cellulosic microparticle occurrences in the NE Atlantic, focusing on the Porcupine Bank Canyon and Porcupine Seabight. Water samples from depths ranging between 605 and 2126 m and Lophelia pertusa coral samples from 950 m depth were analysed. Microparticles were detected in deep-water habitats, with concentrations varying from 2.33 to 9.67 particles L−1 in the Porcupine Bank Canyon, notably lower at greater depths. This challenges the assumption of deeper habitats solely acting as microplastic sinks. We also found evidence of microparticle adsorption and ingestion by L. pertusa. The presence of microparticles in cold-water corals underscores their vulnerability to pollutants. Furthermore, the dominance of rayon microparticles in both water and coral samples raises questions about marine pollution sources, potentially linked to terrestrial origins. This research emphasises the critical need for comprehensive exploration and conservation efforts in deep-sea environments, especially to protect vital ecosystems like L. pertusa reefs.


